-

-
 Whatsapp:+86 17732187393
Whatsapp:+86 17732187393 -


- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- haitian_creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- scottish-gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
large metal plant supports
The Role of Large Metal Plant Supports in Industrial Infrastructure
In the dynamic landscape of modern industry, the structural integrity of facilities is paramount. Among the critical elements that contribute to this integrity are large metal plant supports, which play an indispensable role in the construction and operation of industrial plants. From manufacturing facilities to power plants, these supports are foundational in ensuring that heavy equipment is securely held, enabling efficient production processes while safeguarding worker safety.
Large metal supports come in various forms, including beams, columns, and girders, each designed to withstand significant loads and environmental stressors. The materials used in manufacturing these supports, typically steel or reinforced alloys, are chosen for their strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and resistance to corrosion. For instance, the use of galvanized steel, which is coated to prevent rust, is particularly prevalent in environments that may be exposed to moisture or chemicals, enhancing the lifespan of the structural components.
One of the primary functions of large metal plant supports is load distribution. In industrial settings, machinery, equipment, and storage systems can be exceedingly heavy. Without a robust support system, the weight of these elements could lead to structural failure, posing risks to both personnel and operational continuity. Large metal supports effectively distribute these loads across a wider area, minimizing localized stress and contributing to overall structural stability.
Moreover, large metal supports are integral to the design of modular systems. In contemporary industrial applications, modularity allows for flexibility and adaptability in plant layouts. This is particularly beneficial when companies need to scale operations up or down in response to market demands. By utilizing large metal supports, facilities can more easily adjust their configurations, ensuring that plants remain functional and efficient without undergoing extensive renovations.
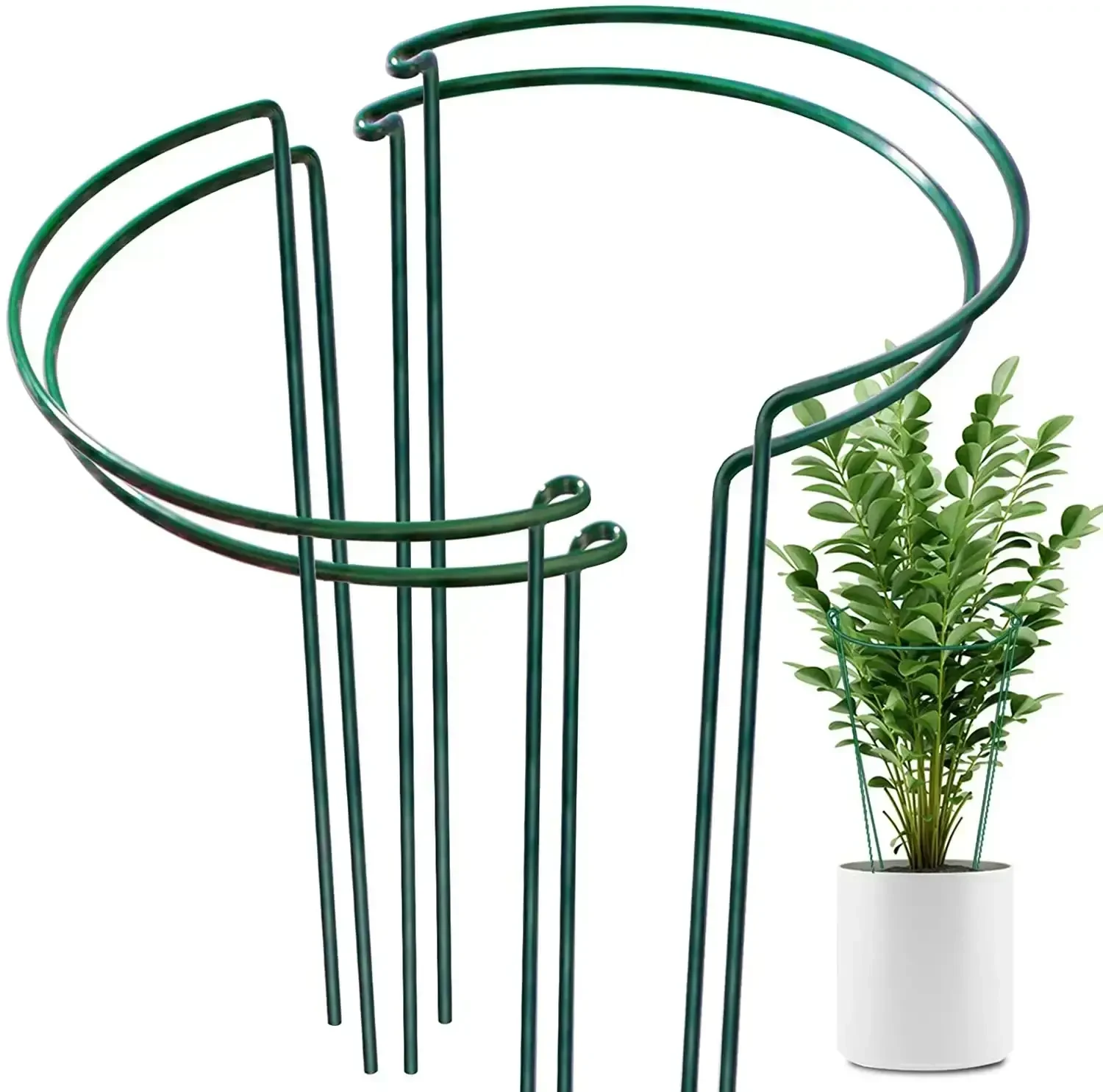
large metal plant supports

In addition to their structural role, large metal supports can also facilitate the integration of various technological systems within industrial plants. For example, the supports can serve as conduits for electrical and plumbing systems, allowing for a cleaner and more organized facility layout. This integration is essential, particularly in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food processing, where hygiene and accessibility to utilities are critical.
Another aspect worth considering is the environmental impact of large metal supports. Many industries are increasingly focusing on sustainability and reducing their carbon footprint. The production of metal supports can incorporate recycled materials, reducing the demand for virgin resources and minimizing waste. Additionally, robust metal supports can prolong the lifespan of industrial infrastructure, reducing the need for frequent replacements and the associated environmental costs.
Safety is an overarching concern in all industrial applications, and large metal plant supports contribute significantly to a safer working environment. By ensuring that heavy equipment is securely anchored and supported, the risk of accidental collapse or equipment failure is greatly diminished. Furthermore, robust supports are often designed to comply with international safety standards and regulations, further ensuring the protection of workers.
As industries evolve, the importance of large metal plant supports is only expected to grow. With advancements in materials science and engineering, future developments may lead to even stronger, lighter, and more sustainable support structures. Innovative designs and manufacturing techniques will likely emerge, enabling new applications and enhanced safety features.
In conclusion, large metal plant supports are a cornerstone of industrial infrastructure. Their ability to provide stability, integrate systems, and enhance safety makes them indispensable in the modern manufacturing landscape. As industries continue to innovate and strive for sustainability, the role of these supports will remain critical, ensuring that industrial plants not only meet today's demands but are also prepared for the challenges of tomorrow.
-
USA Standard Galvanized Movable Chain Link Temporary FenceNewsSep.01,2025
-
Hot Selling Metal Garden Arch for Climbing Plants - Outdoor & BackyardNewsAug.31,2025
-
Golden Circle Round Balloon Arch Frame Kit - Backdrop & Garden ArchNewsAug.30,2025
-
Circular Plant Supports: Sturdy Iron & Half-Circle DesignsNewsAug.29,2025
-
Durable PVC Coated Wire Mesh for Sale | Factory Direct PricesNewsAug.28,2025
-
Coated Chicken Wire for Sale - Durable & Rust-Resistant PVC MeshNewsAug.27,2025